About The Graph (GRT)
The Graph (GRT) is a decentralized protocol designed to index and query data from blockchains, making it easier for developers to access and use blockchain data. Much like how Google indexes and organizes information on the web, The Graph indexes blockchain data from networks such as Ethereum, IPFS, and Filecoin. This data is organized into open APIs called subgraphs, which anyone can query. The Graph facilitates the seamless retrieval of blockchain data for decentralized applications (dApps) in the Web3 ecosystem.
What is The Graph (GRT)?
The Graph is an indexing protocol that serves as the backbone for querying data from blockchains such as Ethereum, IPFS, and POA (Proof of Authority). It enables developers to create and publish open APIs (called subgraphs) that dApps can query using the GraphQL query language.
Key features of The Graph include:
- Indexing Blockchain Data: The Graph indexes blockchain data into subgraphs, making it easily accessible and searchable for developers.
- Open APIs (Subgraphs): Developers can publish subgraphs, which represent the data available for querying.
- Querying with GraphQL: Subgraphs are queried using GraphQL, a query language commonly used for retrieving data.
- Decentralized Infrastructure: The Graph is decentralized, ensuring that data queries are trustless and transparent, and eliminating the need for centralized intermediaries.
The Graph currently supports several major blockchain networks, including Ethereum, IPFS, and POA, and is continuously expanding to integrate additional blockchain networks.
How Does The Graph (GRT) Work?
The Graph uses its native Graph Token (GRT) to power its decentralized network. GRT is an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain and is used for various functions within The Graph ecosystem. The protocol relies on several participants to operate efficiently, including Indexers, Curators, and Delegators. Here’s how it works:
- Indexers:
- Indexers are responsible for indexing blockchain data and making it available for queries.
- They perform the heavy lifting of processing and storing blockchain data into subgraphs.
- Indexers are compensated through indexing rewards and query fees from users who query the subgraphs.
- Curators:
- Curators signal on the subgraphs they believe are valuable by staking GRT tokens.
- They help indicate which subgraphs should be indexed by Indexers, ensuring the quality and relevance of the data.
- Curators receive a portion of the query fees for the subgraphs they signal on.
- Delegators:
- Delegators do not index or curate data directly but can delegate their GRT tokens to Indexers and Curators.
- By delegating their tokens, they indirectly participate in the network and receive a portion of the compensation that Indexers and Curators earn based on their staked GRT.
- Compensation:
- Participants (Indexers, Curators, and Delegators) are compensated for their work based on the amount of GRT they have staked and the services they provide.
- The compensation is proportional to the amount of work done and the stake held by each participant in the network.
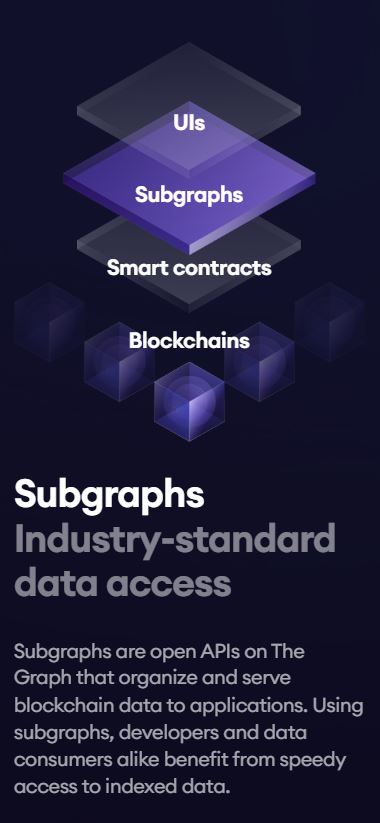
- Subgraphs:
- Subgraphs are open APIs that represent specific datasets on a blockchain. They allow developers to access blockchain data without needing to build custom indexing solutions.
- Subgraphs are open and publicly available, ensuring that the data queried is transparent and accessible to all developers in the ecosystem.
What Are the Potential Use Cases for The Graph (GRT)?
The Graph (GRT) provides a decentralized solution for querying blockchain data, offering several key benefits and use cases:
- Blockchain Data Indexing:
- The Graph enables efficient and reliable indexing of blockchain data, making it accessible to developers. This removes the need for building custom data indexing solutions, saving time and resources.
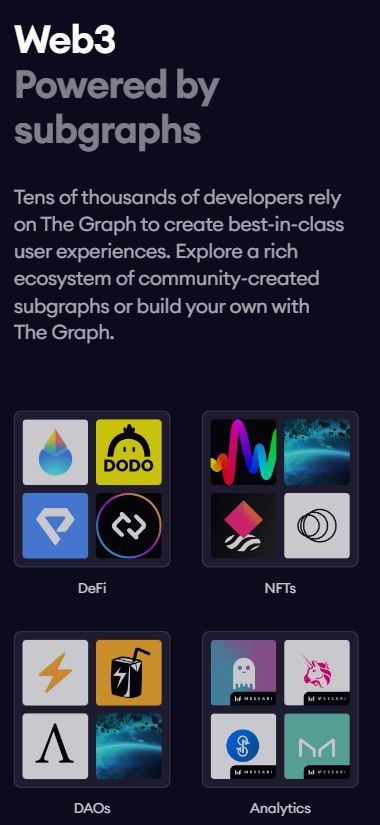
- DApp Development:
- Developers use The Graph to access blockchain data via subgraphs, which simplifies the development of decentralized applications (dApps). Major DeFi platforms and services like Uniswap, AAVE, and Synthetix use The Graph to access data efficiently.
- DeFi Ecosystem:
- The Graph is widely used in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications that need to query transaction data, smart contract states, token balances, liquidity pools, and more. It streamlines the process of accessing this data in real-time.
- NFT Platforms:
- The Graph supports NFT platforms by indexing blockchain data related to NFT ownership, transactions, and metadata, enabling seamless access for marketplaces, galleries, and applications that rely on NFT data.
- Analytics and Data Insights:
- The Graph allows developers to create data-driven applications that pull real-time insights from the blockchain. This enables the development of advanced analytics tools that offer insights into the state of DeFi, NFTs, and other Web3 data.
- Decentralized Infrastructure:
- By decentralizing the indexing and querying process, The Graph ensures the integrity and security of blockchain data, removing the need for centralized intermediaries and providing a trustless infrastructure for querying data.
- Web3 Ecosystem Growth:
- The Graph’s infrastructure plays a key role in the growth of Web3 by offering a robust, decentralized API service that makes blockchain data accessible for a wide range of decentralized applications, projects, and protocols.
What Is the History of The Graph (GRT)?
The Graph was founded in 2018 by Yaniv Tal, Brandon Ramirez, and Jannis Pohlmann, who have backgrounds in engineering and software development. The three founders had worked together previously at MuleSoft, an API developer tools company, and they co-founded The Graph to address the growing need for decentralized data indexing in the blockchain space.
Key milestones in the history of The Graph include:
- 2018: The idea for The Graph was conceived, aiming to create decentralized APIs for blockchain data querying.
- 2020: The Graph was launched and became one of the first decentralized protocols to allow developers to query blockchain data through open APIs (subgraphs).
- 2020-2021: The Graph grew rapidly, with thousands of developers and organizations adopting the protocol. Major projects in the DeFi and NFT spaces, like Uniswap, Synthetix, and AAVE, began to integrate The Graph into their platforms.
- 2021: The Graph Token (GRT) was launched via a public token sale and became integral to the protocol’s decentralized governance and resource allocation system.
- 2021-present: The Graph continues to expand its support for additional blockchain networks and is constantly improving the scalability and efficiency of its infrastructure.
The Graph has received support from the blockchain community, including strategic investments from VCs and influential figures, and it is used by developers and dApp creators around the world. Its protocol is fully open-source, which aligns with the broader ethos of decentralization and transparency in the Web3 ecosystem.





















Harran –
👍
judyharran –
👍