About Fantom (FTM)
What is Fantom (FTM)?
Fantom (FTM) is a decentralized, open-source smart contract platform designed to provide high-performance decentralized finance (DeFi) services. It aims to overcome the limitations of previous-generation blockchains, such as scalability and high transaction fees, by leveraging innovative consensus mechanisms and technologies. Fantom is built to be an alternative to Ethereum, with a focus on speed, security, and decentralization, while offering a significantly more scalable and cost-efficient infrastructure. The native token of the Fantom network, FTM, is used for payments, staking, governance, and network fees, powering the ecosystem.
Fantom’s key differentiator is its use of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure, allowing the network to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS) with low fees and short confirmation times. This makes it particularly suitable for decentralized applications (DApps), digital assets, and other high-volume transaction requirements.
How Does Fantom (FTM) Work?
Fantom operates using two main components that ensure scalability, speed, and security:
- Lachesis Protocol:
- The Lachesis protocol is the core consensus mechanism behind Fantom. It is an Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (aBFT) Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithm that uses Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) technology.
- In a DAG, data transactions do not have to be processed in a strict sequential order, which allows for greater parallel processing and faster validation of transactions. This results in a much higher transaction throughput compared to traditional blockchain structures.
- aBFT ensures that the system remains secure and fault-tolerant, even if some participants in the network act maliciously or fail to operate properly.
- The aBFT PoS consensus mechanism allows validators to secure the network while maintaining efficiency at high speeds, making the Fantom network fast and scalable.
- Opera:
- Opera is Fantom’s mainnet and application development layer. It is the smart contract platform that hosts DApps (decentralized applications).
- Opera also operates using the PoS model, but it employs leaderless validators for added security and decentralization.
- The platform enables developers to easily build and deploy smart contracts while enjoying low fees and fast processing times.
- Opera‘s integration with the Lachesis protocol ensures that the network can handle large volumes of transactions in a highly decentralized and efficient manner.
Key Features of Fantom:
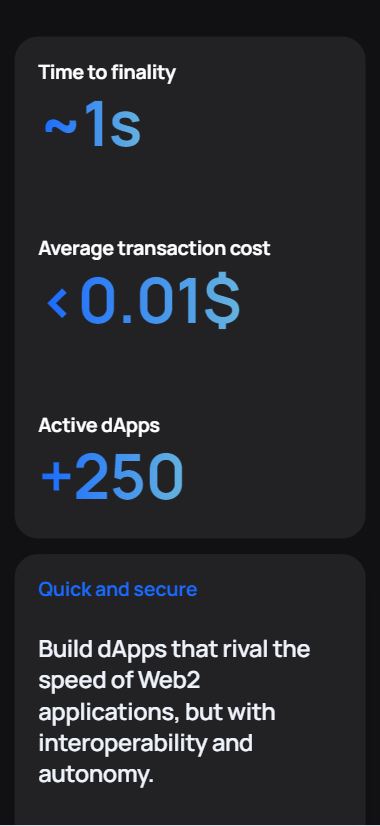
- Scalability: Fantom can process thousands of transactions per second (TPS), enabling it to handle large-scale decentralized applications and financial services.
- Low Fees: The network is optimized for low transaction fees (fractions of a cent per transaction), making it a cost-effective choice for users and developers.
- Fast Transactions: Transactions on Fantom are settled in 1-2 seconds, ensuring quick confirmation times for DApps and users.
- On-chain Governance: FTM token holders have the ability to participate in governance decisions, such as voting on upgrades, protocol changes, or future proposals for the Fantom network.
What Are the Potential Use Cases for Fantom (FTM)?
Fantom’s high-performance features make it suitable for a wide range of use cases, including:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
- Fantom is well-suited to DeFi applications due to its high scalability, low fees, and fast transaction times. DeFi projects on Fantom can process transactions quickly and at a much lower cost compared to other blockchains, which is crucial for trading, lending, and borrowing.
- Fantom also offers a suite of built-in DeFi instruments that simplify the development and integration of decentralized financial applications.
- Decentralized Applications (DApps):
- Fantom provides an efficient and scalable platform for developers to build and deploy DApps. The combination of high throughput and low transaction costs makes it an attractive platform for a wide range of applications in sectors such as gaming, NFTs, and supply chain management.
- Staking:
- FTM token holders can participate in staking, where they lock their tokens to secure the network and earn rewards. The PoS model ensures that validators play a crucial role in maintaining the security and decentralization of the network.
- Governance:
- Fantom operates on an on-chain governance model where FTM holders can vote on proposals that shape the future of the platform. This gives the community the power to propose changes, upgrades, or modifications to the protocol.
- Cross-chain Interoperability:
- Fantom aims to create cross-chain compatibility, enabling smooth interaction between different blockchains and allowing users and developers to move assets and data across various networks. This is especially important as the crypto ecosystem grows and becomes more fragmented.
What is the History of Fantom (FTM)?
The Fantom Foundation was established in 2018 by South Korean computer scientist Dr. Ahn Byung Ik. The goal was to create a smart contract platform that could overcome the limitations of existing blockchain solutions, such as scalability, high fees, and slow transaction times.
- 2018: The Fantom team raised funds through token sales to support the platform’s development.
- 2019: Fantom launched its mainnet, called OPERA, which marked the first live deployment of the network.
- 2020–2021: The platform continued to grow, attracting DApp developers and DeFi projects seeking to benefit from its high scalability and low fees.
- 2023: Fantom has established itself as a major player in the DeFi space, hosting a variety of DApps, decentralized finance protocols, and other blockchain-based services.
As of 2023, Fantom has a total supply of 3.175 billion FTM tokens, a portion of which are in circulation. The rest of the tokens are released gradually over time according to a predefined schedule.
FTM Token Utility
The FTM token powers the Fantom ecosystem, with various use cases:
- Staking: Users can stake FTM tokens to become validators or participate in the PoS consensus mechanism.
- Payments: FTM is used to pay for transaction fees on the Fantom network.
- Governance: FTM holders can vote on proposals that affect the direction and operation of the Fantom platform.
- Network Security: FTM helps secure the network through the staking process, where validators lock up their FTM tokens to support the integrity and operation of the network.



















Harran –
good
Eyad –
‘