About EOS
What is EOS?
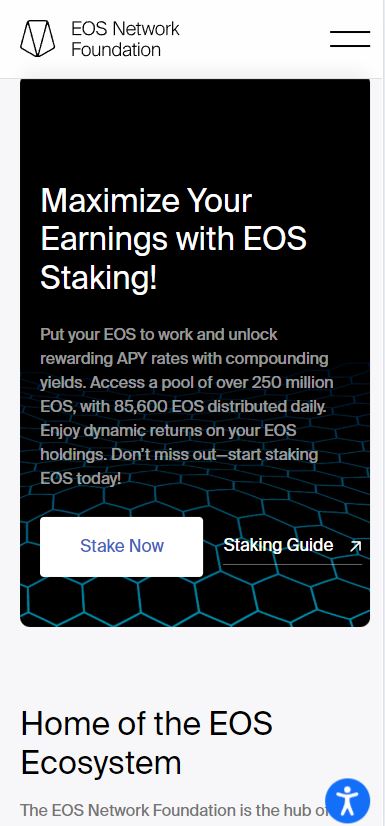
EOS is an open-source blockchain platform designed to support large-scale decentralized applications (DApps) with high performance, flexibility, and scalability. The platform is unique in that it eliminates transaction fees, relying instead on periodic rewards to entities running the network, effectively substituting inflation for transaction costs. EOS uses the EOS virtual machine and an extensible WebAssembly engine for executing nearly fee-less transactions, offering developers a highly efficient environment for building applications. Powered by a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, EOS decentralizes authority by allowing stakeholders to elect node operators who validate transactions.
How does EOS work?
EOS operates on a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus model, where token holders elect delegates (block producers) responsible for validating transactions and maintaining the network. This system reduces the risk of centralization often associated with Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains, where mining power is concentrated in the hands of a few large players. In EOS, token holders also share in the governance of the network, giving them voting power over key decisions, such as network upgrades. EOS’s design allows for the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) with high throughput, near-instant finality, and no transaction fees, providing a highly scalable and efficient platform for developers.
What are the potential use cases for EOS?
EOS is designed to address the challenges that other blockchain platforms face when supporting large-scale applications. Its high scalability, no transaction fees, and low latency make it particularly suitable for building decentralized applications (DApps) across industries such as finance, gaming, supply chain, and social networks. The platform is also ideal for creating smart contracts and tokenized platforms, offering developers the flexibility to build custom blockchain infrastructures. The decentralized governance model ensures that the EOS network is user-driven and community-oriented, making it an attractive option for developers seeking a platform with both technical and community support. EOS can also be used to support decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), digital identity systems, and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
What is the history of EOS?
EOS was developed by Block.one, a blockchain technology company led by architect Daniel Larimer, who is also known for his contributions to other projects like Steemit and BitShares. The EOSIO software, which powers the EOS Network, was designed to offer a more scalable alternative to Ethereum and other blockchain platforms. EOS launched in June 2018 after a year-long Initial Coin Offering (ICO) that raised over $4 billion, making it one of the largest ICOs in history. The launch was followed by the establishment of the EOS Network Foundation (ENF), a non-profit organization aimed at supporting the growth and development of the EOS ecosystem. The ENF was created following a consensus among EOS block producers and is focused on providing financial and non-financial resources to help the EOS community thrive.





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.