Article on Blockchain and its Types
Introduction:
Blockchain is a technology that enables the decentralized and secure storage and transmission of data across a network of computers. In essence, a blockchain is a digital ledger in which transactions are recorded in blocks and linked together in a chain. These blocks are secured using cryptography, making it extremely difficult to alter or tamper with any recorded data.Components of Blockchain:
Blocks: Each block contains a group of encrypted transactions.
Chain: A series of connected blocks.
Nodes: Computers connected to the network that hold a copy of the ledger.
How Blockchain Works:
When a new transaction occurs, it is verified by multiple nodes across the network. Once verified, the transaction is added to a new block, which is then linked to the previous blocks, forming a chain. Altering any previous transaction would require changing all subsequent blocks, which requires enormous computing power, making the system highly secure.Types of Blockchain:
Public Blockchain: Public blockchains are open networks where anyone can join and participate in transaction verification. Popular examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum.Advantages: High transparency, fully decentralized.
Disadvantages: High energy consumption and limited scalability due to the volume of transactions.
Private Blockchain: These blockchains are restricted and governed by a single organization or a group of authorized users. They are commonly used by companies.Advantages: More efficient and faster than public blockchains.
Disadvantages: Less transparent and less decentralized.
Hybrid Blockchain: Combines elements of both public and private blockchains. Certain parts of the network are open to the public, while others are restricted to authorized users.Advantages: Offers greater flexibility in data control.
Disadvantages: More complex to manage.
Consortium Blockchain: This type is similar to a private blockchain but is managed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity.Advantages: Facilitates cooperation between companies while maintaining security.
Disadvantages: Requires complete consensus between participants.
Blockchain Applications:
Cryptocurrencies: Such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Smart Contracts: Automated contract execution without intermediaries.
Supply Chain Management: Used to track shipments and ensure the integrity of logistical processes.
Electronic Voting: Ensures transparency and security in voting systems.
Conclusion:
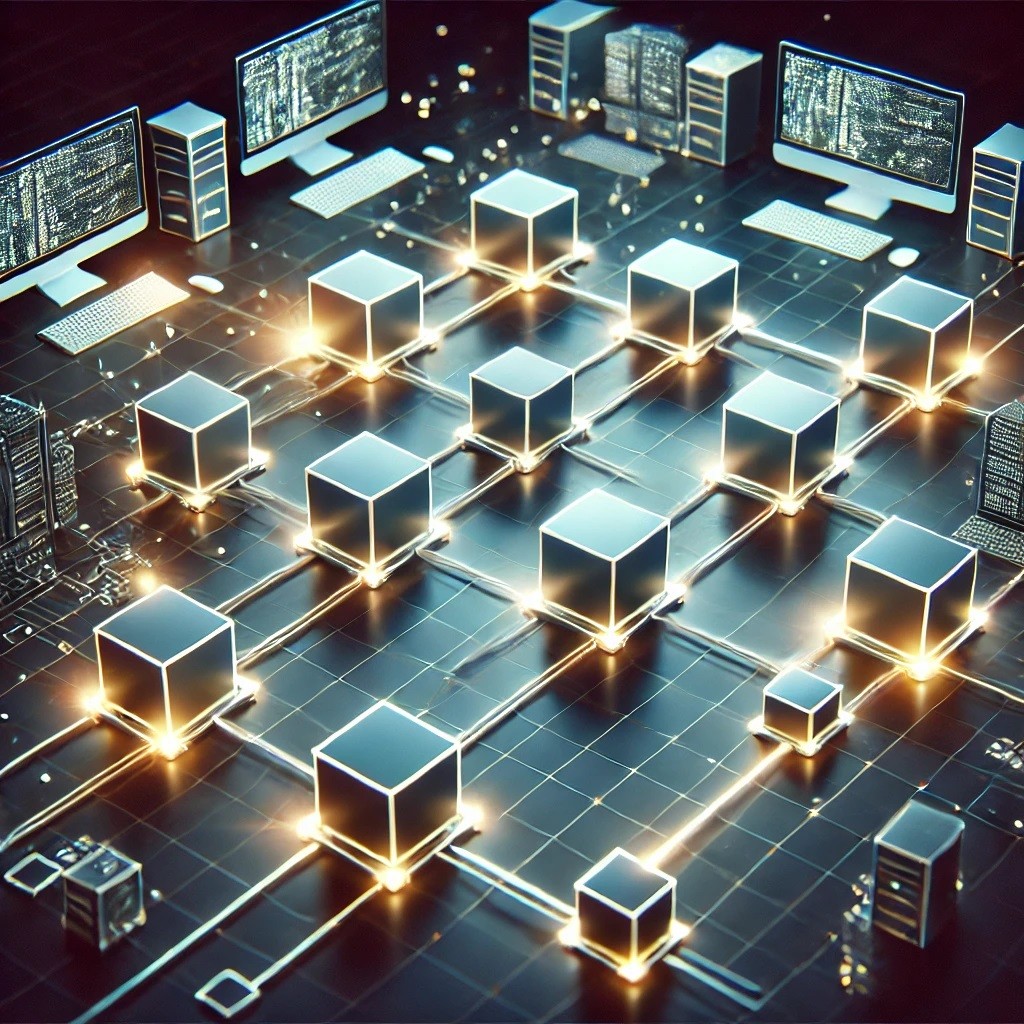
Blockchain technology is one of the most transformative innovations in recent years. With its ability to secure data and ensure transparency, it is poised to revolutionize a variety of fields, from digital currencies to smart contracts and beyond.Conceptual Image:
I’ve created a visual representation of a blockchain network, showing interconnected blocks and nodes symbolizing the decentralized and secure nature of blockchain technology. You can view the image above.
User Balance
178,920
/
Tokens Legend
Legend
 Legend
LegendUser Badges
About Me

Mahmoud Harran
Egypt
Media
Photos
Videos
Audios
Files
Friends
اصيل عاطف
@aseelatef413
yeneyannick1999
@yeneyannick1999
Adamu Yarima
@adamuyarima
Yan Bakter
@bachter12
Mkangafu255
@acolytemuhembano

 Français
Français Português
Português Indonesia
Indonesia Tagalog
Tagalog Malaysia
Malaysia हिन्दी
हिन्दी বাংলা
বাংলা 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt