About Flux
What is Flux?
Flux is a cryptocurrency and decentralized platform designed to support the development, deployment, and operation of the Web3 ecosystem, also known as the decentralized Internet of the future. The Flux ecosystem is composed of several core components:
- $FLUX Token: The native, minable Proof-of-Work (PoW) cryptocurrency used within the Flux network.
- Flux Network (FluxNodes): A decentralized network of nodes that contribute computing power to support the decentralized infrastructure.
- FluxOS: A Linux-based operating system that powers decentralized applications (DApps) within the Flux ecosystem.
- Zelcore: A digital asset platform for managing crypto assets across multiple blockchains and providing access to Web3 applications.
- Flux Blockchain: A blockchain designed for on-chain governance, economics, and parallel assets, facilitating interoperability with other blockchains and DeFi (decentralized finance) access.
Flux’s mission is to create a decentralized Web3 infrastructure, focusing on reducing single points of failure, improving system uptime, and tackling the sustainability issues often associated with traditional Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains. Flux aims to transform how blockchain technology is used by leveraging its decentralized network to power critical applications in Web3.
How Does Flux Work?
Flux operates through several key mechanisms and technologies:
- Decentralized Network of Nodes (FluxNodes):
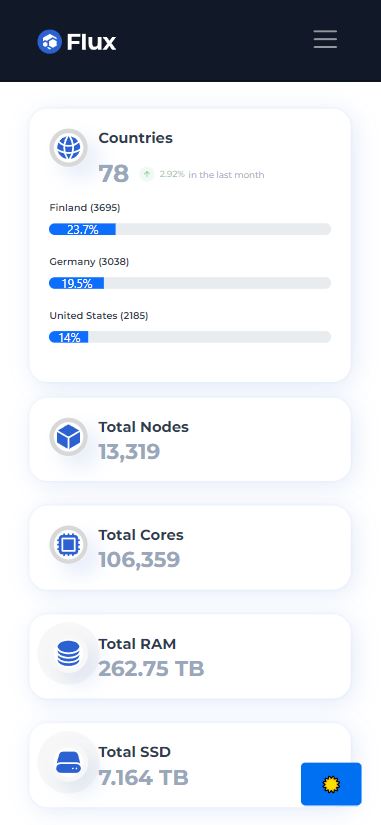
- Flux utilizes a network of decentralized FluxNodes that are run by users worldwide. These nodes contribute computing power and storage to the Flux ecosystem, ensuring its decentralized nature.
- The decentralized nodes work together to secure the network and provide computing resources for running applications and services in Web3.
- Parallel Assets:
- Parallel Assets are a feature of Flux that enables the transfer of assets between different blockchains. This interoperability allows cross-chain functionality, allowing assets to be ported from one blockchain to another seamlessly.
- This system enables developers to run decentralized applications (DApps) on any blockchain while leveraging Flux’s decentralized infrastructure, making it a highly flexible and scalable platform for Web3 development.
- Proof of Useful Work (PoUW):
- Unlike traditional Proof of Work (PoW) systems, which use vast amounts of computing power to solve random, non-useful problems, Flux introduces Proof of Useful Work (PoUW).
- PoUW utilizes GPU miners to perform meaningful, real-world tasks, such as video encoding, weather predictions, or assisting with machine learning models. This makes Flux’s network not only energy-efficient but also impactful, addressing concerns over the environmental impact of traditional PoW systems.
- On-Chain Staking:
- Flux provides staking mechanisms through Titan nodes and other platforms, enabling users to stake their $FLUX tokens and earn rewards for their participation in securing and maintaining the network.
- Users can also stake their Flux tokens to support various applications, contributing to the overall security and decentralization of the platform.
- FluxOS:
- FluxOS is a Linux-based operating system designed specifically for decentralized computing. It enables developers to deploy and manage decentralized applications (DApps) with greater ease and flexibility.
- With FluxOS, developers have access to a set of tools and infrastructure that supports Web3 applications, ensuring high uptime and security across the decentralized network.
What are the Potential Use Cases for Flux?
Flux has a wide range of potential use cases, driven by its powerful decentralized network and infrastructure capabilities. Some of the key use cases include:
- Decentralized Hosting and Computing:
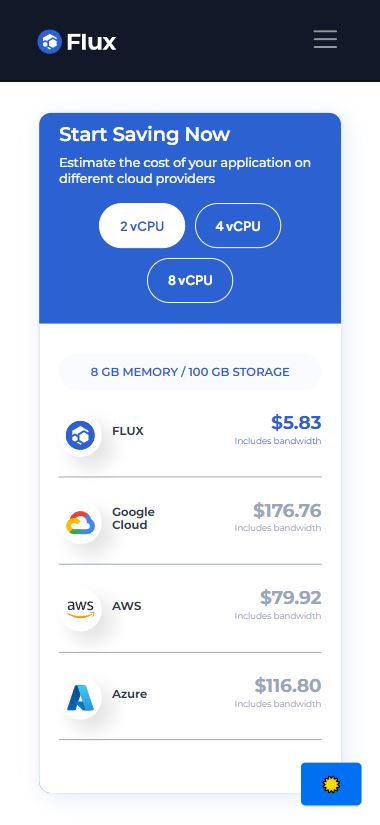
- Flux provides an alternative to traditional cloud services by offering decentralized computing power through its network of FluxNodes. Developers can use Flux to host decentralized applications (DApps) and leverage a decentralized computing network for scalable infrastructure.
- This also eliminates single points of failure, increasing uptime and resilience for Web3 applications.
- Interoperability with Other Blockchains:
- Through Parallel Assets, Flux enables assets to move seamlessly between different blockchains, creating a cross-chain ecosystem. This helps developers build multi-chain decentralized applications that can access resources from multiple blockchains without limitations.
- Flux supports various blockchains like Flux-Kadena, Flux-ETH, and Flux-BSC, enabling users and developers to operate within a multi-chain environment.
- Proof of Useful Work (PoUW) Applications:
- Flux’s unique Proof of Useful Work (PoUW) mechanism opens the door for solving real-world problems using the computational power of its miners. This could include applications in industries like artificial intelligence, weather forecasting, healthcare, video streaming, and research.
- For example, Flux miners could assist research teams with machine learning models, help encode videos for media platforms, or contribute to environmental studies.
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance):
- With Flux’s infrastructure and interoperability, it has the potential to become a major player in the DeFi space. Developers can deploy DeFi protocols and applications on the Flux network, taking advantage of its decentralized computational power, staking options, and cross-chain capabilities.
- Flux aims to provide high uptime and low-cost alternatives to existing centralized DeFi solutions, making it an attractive platform for building and using DeFi applications.
- Energy-Efficient Blockchain:
- With its Proof of Useful Work (PoUW) mechanism, Flux addresses one of the major criticisms of traditional Proof of Work systems: the high energy consumption. Flux miners contribute to meaningful and real-world tasks, reducing unnecessary energy usage and providing a more sustainable blockchain model.
- Web3 Infrastructure:
- Flux’s platform is built specifically to support Web3 applications. It offers a comprehensive ecosystem for developers to deploy decentralized applications, run blockchain-based services, and integrate Web3 functionalities without relying on centralized infrastructure providers.
What is the History of Flux?
Flux was co-founded by Daniel Keller, Tadeas Kmenta, and Parker Honeyman, who bring extensive experience in technology infrastructure and large-scale project leadership.
- Flux was designed from the ground up to be a decentralized and energy-efficient alternative to traditional blockchain systems.
- The project was GPU mined since its inception, with no ICO or IEO (initial coin offering or initial exchange offering), giving it a fair and decentralized start.
- The Flux ecosystem has grown to include a range of innovative components such as FluxNodes, FluxOS, and Zelcore, as well as several parallel assets like Flux-Kadena, Flux-ETH, and Flux-BSC.
- Flux has partnered with Nvidia’s Inception Program, Seeed Studio, Lumen Technologies, and OVHcloud, to push the development of Web3 technologies and expand the use of its platform in the global tech ecosystem.
Flux’s commitment to decentralization, energy efficiency, and cross-chain interoperability makes it a strong player in the Web3 and decentralized Internet space.


















Harran –
👍👍👍
Eyad –
👍